The Importance of Infection Control in Phlebotomy
- Phlebotomy Technician
- March 12, 2024
- 4.2k views
- 4 min read
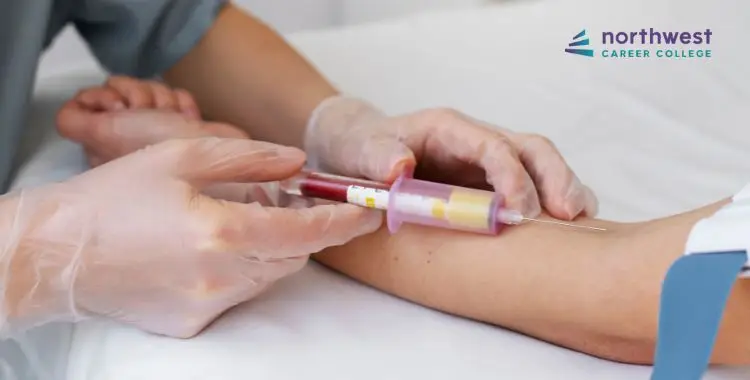
Venipuncture and other specimen collection services provided by phlebotomy technicians represent a critical part of the healthcare industry. Specifically, these procedures offer healthcare providers the opportunity to significantly enhance their diagnostic capabilities. However, because many of the procedures performed by phlebotomists are invasive in nature, infection control is paramount to ensure the safety of patients.
Table of Contents
Understanding Infection Control in Phlebotomy
Venipuncture presents risks for the spread of bloodborne diseases if not performed in accordance with infection control best practices. In this article, we will explore some of the most critical ways that phlebotomy technicians can prevent the spread of disease during the blood collection process. Such infection control measures not only protect patients but also safeguard the healthcare professionals who serve them and the community at large.
Key Infection Control Practices for Phlebotomists
Hand Hygiene
Effective infection control protocols start with proper hand hygiene. Hands are the primary mode of disease transmission for many common infections. Proper hand hygiene significantly reduces this risk during phlebotomy procedures.
Ideally, all healthcare providers should thoroughly wash their hands before initiating a patient encounter. Alternatively, they may use hand sanitizer between patients when washing their hands is not reasonably achievable.
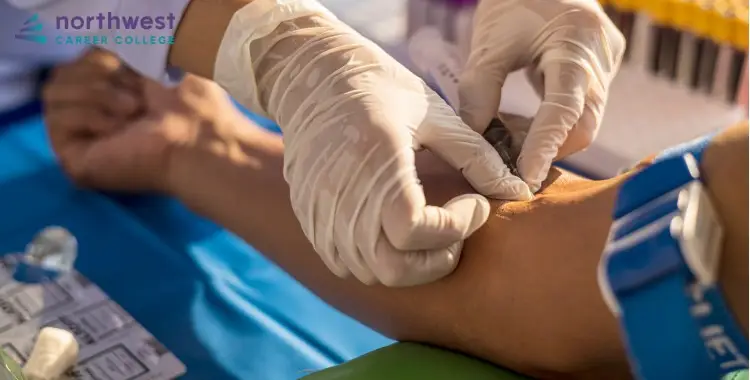
Infection control procedures during venipuncture and other phlebotomy services include the use of gloves by phlebotomists, the use of sterile and single-use equipment such as needles and tubes during blood collection procedures, and the use of specialized biohazard and sharps containers to dispose of materials after blood collection is complete.
Personal Protective Equiment
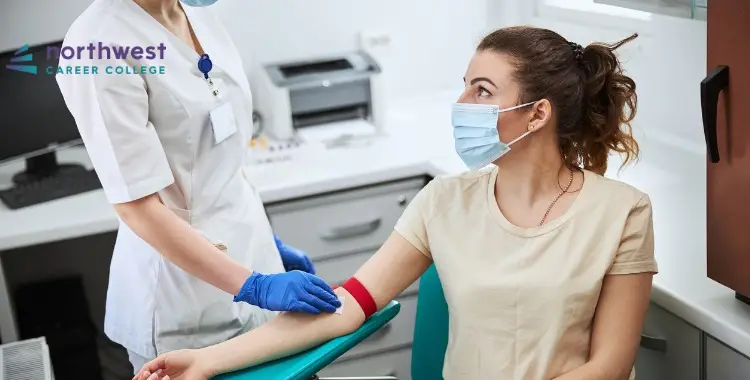
In addition to hand hygiene, the use of personal protective equipment is very effective at reducing infection transmission. Specifically, the use of gloves during venipuncture and other phlebotomy procedures reduces the risk of transmission.
After washing their hands, phlebotomy technicians should don their gloves in front of the patient while inside the treatment room. Doing so reassures the patient that the gloves are fresh, clean, and able to provide an effective barrier against disease transmission. The use of gloves also protects the phlebotomy technicians, as patients may have pathogens on their skin that could put the technician at risk.
Sterile Equipment
Phlebotomy technicians use sterile, single-use needles and tubes to complete phlebotomy procedures. By doing so, they reduce the risk of infection being transmitted via the surface of their equipment.
Given that needles directly enter the bloodstream and that the inside of vacutainer tubes establish a direct connection with the bloodstream via the needle and tube holder, it is imperative that these items are sterile at the time they are used.
Disposal of contaminated materials
Phlebotomy technicians must carefully dispose of all materials used during phlebotomy procedures. Single-use needles must be removed from the tube holder, closed with one hand only, and disposed of in an approved sharps container. Any gauze saturated with blood or other bodily fluids must be disposed of in a biohazard container. These practices minimize the risk of disease transmission after the conclusion of the venipuncture.
Training and Education for Phlebotomists
Proper infection control starts in the classroom. Phlebotomy technicians must be taught how to use infection control best practices from the first day of their training. This is why going to an accredited program is typically the best choice available to aspiring phlebotomy students, as they can rest assured that the quality of their curriculum has been assessed by a trusted third party.
Additionally, most states require phlebotomy technicians to obtain national certification before pursuing licensure. Certification requires candidates to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of industry best practices, including infection control expectations, before delivering patient care.
Finally, phlebotomy technicians are required to participate in ongoing continued education to maintain their certification and licensure. By staying current with up-to-date infection control protocols, they can maintain a high standard of care in the various healthcare settings where they work. This is crucial for patient safety and confidence in the system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, infection control in phlebotomy procedures is of vital importance to maintaining a high standard of care for patients. Such practices minimize the risk of disease transmission from patient to patient, technician to patient, or patient to technician, all of which are possible in the absence of an effective infection control process.
Phlebotomists work in most major medical settings to provide vital services that enable high-quality diagnostic evaluations by healthcare providers. It is crucial that these services continue to be delivered in a safe and effective manner, as they are some of the most important tools that physicians have at their disposal.
When healthcare professionals (such as phlebotomy technicians) and patients adhere to infection control measures, it promotes a safer healthcare environment for everyone.